

Next: Simple nonlinear noise reduction
Up: Practical implementation of nonlinear
Previous: Global function fits
Filtering of signals from nonlinear systems requires the use of special
methods since the usual spectral or other linear filters may interact
unfavorably with the nonlinear structure. Irregular signals from nonlinear
sources exhibit genuine broad band spectra and there is no justification to
identify any continuous component in the spectrum as noise. Nonlinear noise
reduction does not rely on frequency information in order to define the
distinction between signal and noise. Instead, structure in the reconstructed
phase space will be exploited. General serial dependencies among the
measurements 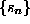 will cause the delay vectors
will cause the delay vectors 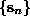 to fill the
available m-dimensional embedding space in an inhomogeneous way. Linearly
correlated Gaussian random variables will for example be distributed according
to an anisotropic multivariate Gaussian distribution. Linear geometric
filtering in phase space seeks to identify the principal directions of this
distribution and project onto them, see Sec.
to fill the
available m-dimensional embedding space in an inhomogeneous way. Linearly
correlated Gaussian random variables will for example be distributed according
to an anisotropic multivariate Gaussian distribution. Linear geometric
filtering in phase space seeks to identify the principal directions of this
distribution and project onto them, see Sec.  . Nonlinear
noise reduction takes into account that nonlinear signals will form curved
structures in delay space. In particular, noisy deterministic signals
form smeared-out lower dimensional manifolds. Nonlinear phase space filtering
seeks to identify such structures and project onto them in order to reduce
noise.
. Nonlinear
noise reduction takes into account that nonlinear signals will form curved
structures in delay space. In particular, noisy deterministic signals
form smeared-out lower dimensional manifolds. Nonlinear phase space filtering
seeks to identify such structures and project onto them in order to reduce
noise.
There is a rich literature on nonlinear noise reduction methods. Two articles
of review character are available, one by Kostelich and Schreiber [57],
and one by Davies [58]. We refer the reader to these articles for
further references and for the discussion of approaches not described in the
present article. Here we want to concentrate on two approaches that represent
the geometric structure in phase space by local approximation. The first and
simplest does so to constant order, the more sophisticated uses local linear
subspaces plus curvature corrections.


Next: Simple nonlinear noise reduction
Up: Practical implementation of nonlinear
Previous: Global function fits
Thomas Schreiber
Wed Jan 6 15:38:27 CET 1999